Ray Diagram Real Image . the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. The main difference between real and virtual images lies in the way in which they are produced. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. Determine focal length and magnification given. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,.
from www.doubtnut.com
The main difference between real and virtual images lies in the way in which they are produced. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Determine focal length and magnification given. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at.
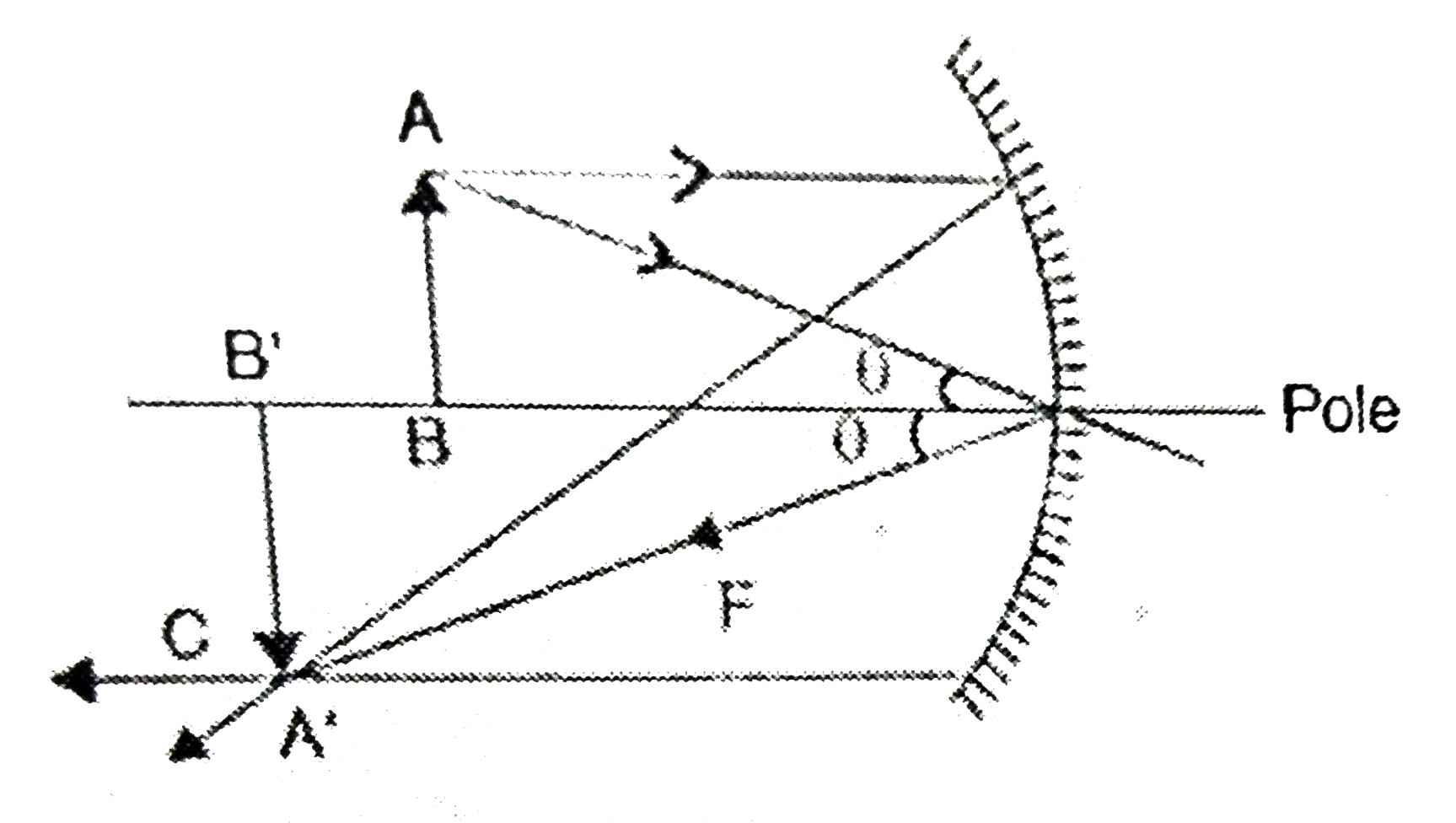
(a) Draw a ray diagram to show image fromation when the concave mirro
Ray Diagram Real Image Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. The main difference between real and virtual images lies in the way in which they are produced. Determine focal length and magnification given.
From cevmpjyh.blob.core.windows.net
Lens Diagram Ray at Stephen Batts blog Ray Diagram Real Image Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From www.teachoo.com
Concave Lens Ray diagram, Images Formed with Steps Teachoo Ray Diagram Real Image explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. a real image. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From www.themetapictures.com
Difference Between Real And Virtual Image Class 10 the meta pictures Ray Diagram Real Image a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. The main difference between real and virtual images lies in the way in which they are produced. Determine. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From revepinphdi.blogspot.com
Draw A Ray Diagram For The Following Situation An Object Far From The Lens Diagram Resource Ray Diagram Real Image Once through the lens, the ray should pass. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Determine focal length and magnification given. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. Determine focal length and magnification given. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From www.wikihow.com
5 Ways to Use a Ray Diagram wikiHow Ray Diagram Real Image a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. Determine focal length and magnification given. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. the image in which light rays from. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From www.youtube.com
REPRESENTATION OF IMAGES FORMED BY SPHERICAL MIRRORS USING RAY DIAGRAMS YouTube Ray Diagram Real Image a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. the image in which light rays. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From www.askiitians.com
Light Reflection and Refraction CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 10 Ray Diagram Real Image Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. a real image and a virtual image. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From guidelibsolidarity.z21.web.core.windows.net
Ray Diagram For Convex And Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Real Image Determine focal length and magnification given. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. The main difference between real and virtual images lies in the way in which they are produced. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. a. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From www.youtube.com
How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10 Physics// YouTube Ray Diagram Real Image Determine focal length and magnification given. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From wiredatapoliciaj0.z22.web.core.windows.net
Ray Diagram Convex Lens Ray Diagram Real Image explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From mydiagram.online
[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams Ray Diagram Real Image explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From mydiagram.online
[DIAGRAM] Convex Mirror Ray Diagram Real Image Ray Diagram Real Image a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. Determine focal length and magnification given. Draw. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From circuitwiringblunts77.z22.web.core.windows.net
Physics Ray Diagrams Ray Diagram Real Image Once through the lens, the ray should pass. Determine focal length and magnification given. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From ecikai.blogspot.com
Ray diagram for an object placed between F and 2F of a convex lens Ray Diagram Real Image explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Once through the lens, the ray should pass. The. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From manuallistaeschylus.z14.web.core.windows.net
Ray Diagram Of Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Real Image explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Determine focal length and magnification given. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature,. a real. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From schematicahortidascv.z21.web.core.windows.net
Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Ray Diagram Real Image Determine focal length and magnification given. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From quizlet.com
5. Ray Diagram Convex Lens Real Image Diagram Quizlet Ray Diagram Real Image a sharp real image (an image that can be displayed on a screen) is formed when all rays from one point on an object arrive at. the image in which light rays from one point on the object actually cross at the location of the image and can be projected onto a screen, a piece of. explain. Ray Diagram Real Image.
From byjus.com
Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed between Ray Diagram Real Image Once through the lens, the ray should pass. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. a real image and a virtual image are different forms of image. the image in which light rays from one point on the object. Ray Diagram Real Image.